
It’s time to fire up Vncviewer and connect to your VNC Server.Īny VNC viewer, including TigerVNC, TightVNC, RealVNC, UltraVNC, Vinagre, and VNC Viewer for Google Chrome, can be used. Verify that the service is successfully started with: $ sudo systemctl status Connecting to VNC server Run the following command to start the VNC service: $ sudo systemctl start Because we are using 1 in the previous section, the VNC server will listen on port 5901. The display port on which the VNC service will run is defined by the number 1 after the symbol. Next, enable the service: $ sudo systemctl enable Run the following command to tell systemd that a new file has been created: $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/ ĮxecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'ĮxecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver :%i -geometry 1440x900 -alwaysshared -fg Remember to modify the username on line 7 to match your own. We can easily start, stop, and restart the VNC service using the systemd unit file.Ĭopy the following settings into your text editor and paste it in.

To ensure that permissions are right, use the following chmod command: $ chmod u+x ~/.vnc/xstartup Creating a Systemd unit file

When you start or restart the TigerVNC server, the script above will be run automatically.Įxecute permissions are also required for the /.vnc/xstartup file. Save and close the file when you’re finished. Create the following file to do so: $ vim ~/.vnc/xstartup
We need to setup TigerVNC to use Xfce now that both Xfce and TigerVNC are installed on the workstation. Because the server is listening on port 5901 (:1) in this example, we’ll shut it down with: $ vncserver -kill :1 Configuring VNC Server Stop the VNC instance using the vncserver command with the -kill option and the server number as an argument before moving on to the next step. It’s worth noting that while working with VNC servers,:X corresponds to 5900+X as a display port. If you use vncserver to create a second instance, it will run on the next available port, which is 2, which means the server will be running on port 5902 (5900+2). The server is listening on TCP port 5901 (5900+1) in our case. This is the number of the display port where the vnc server is running. In the output above, take note of the:1 after the hostname. The password file is created and stored in the /.vnc directory when you run the vncserver command for the first time. The user will not be able to interact with the VNC instance with the mouse or keyboard if you opt to set up a view-only password. You’ll be asked to enter and confirm your password, as well as whether you want it to be view-only.
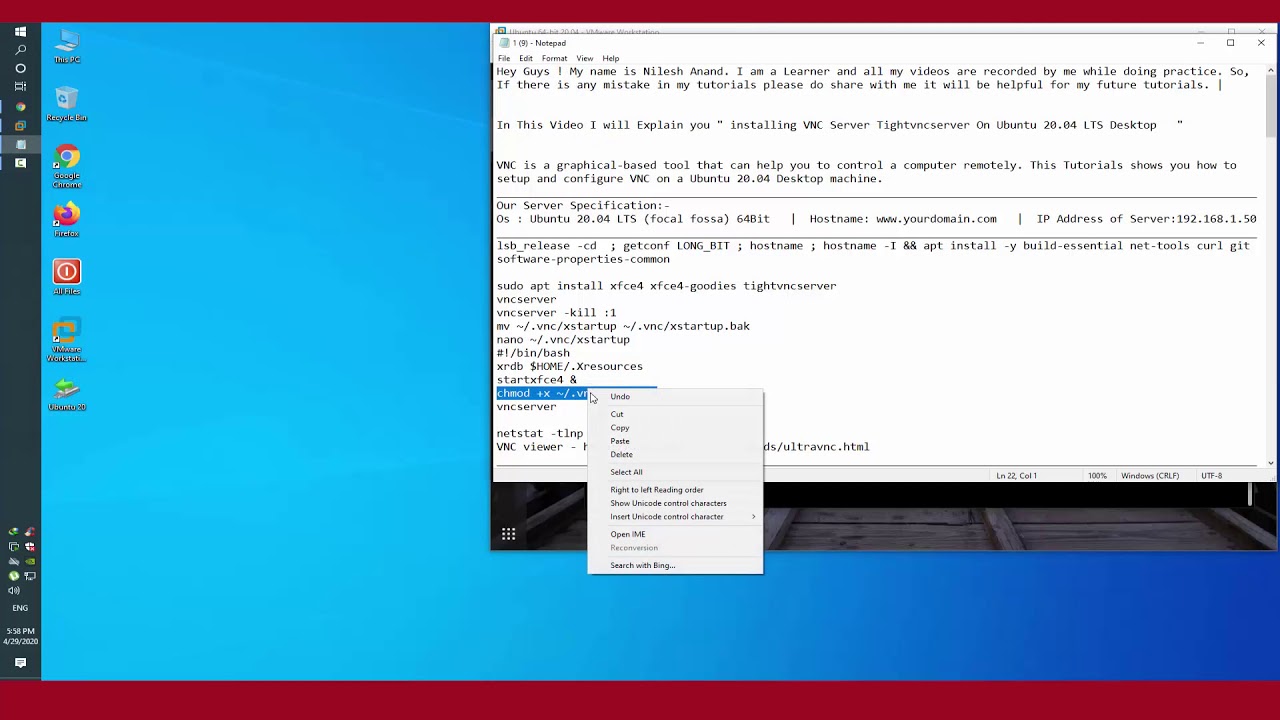
Do not use sudo when running the following command: $ vncserver Once the VNC server is installed, run the vncserver command to create the initial configuration and set up the password.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
